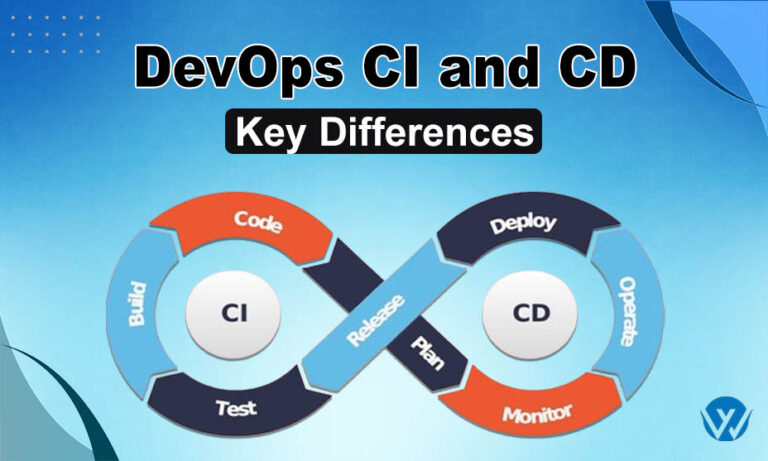
CI and CD are two acronyms: CI stands for Continuous Integration, and CD stands for Continuous Delivery. Under CI, developers merge the code changes into central storage where automated tests run. The CD is the conservatory of Continuous Integration, and it automatically organizes all code changes to a testing and production environment after the development stage. Continuous deployment is more advanced than constant delivery. In this, each change, after going through all production changes, is released to the customers. No human intervention is involved after initiation.
Key differences are also listed in periodic format along with details in the below sections.
| Aspect | Continuous Integration (CI) | Continuous Delivery (CD) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | CI is a process where code changes are frequently integrated into a shared repository, followed by testing. | CD focuses on automating the delivery of integrated code to the desired environment for potential release. |
| Primary Goal | Ensure that software can be released with confidence at any time. | The CD focuses on automating the delivery of integrated code to the desired environment for potential release. |
| Scope Frequency of Execution | The CD focuses on automating the delivery of integrated code to the desired environment for potential release. | CD encompasses the entire process from integration to deployment. |
| Deployment | Frequent (e.g., after every code commit). | Continuous (e.g., automated deployment to staging or production). |
| Decision | CI does not make deployment decisions; it only ensures code quality. | Ensure that software can be released with confidence at any time. |
Continuous Integration (CI)
Continuous integration merges the working copies or updates to a central server daily. Usually, it is implemented with the capability of initiation of automated build with testing. It enables the avoidance of integration challenges at the time of release. The following are the main critical points of continuous integration.
Key Features of Continuous Integration:
Some of the key features are given in detail below.
1. Automated tests for Every Feature:
Developers must write automated tests for every new feature, development, or bug fix. Writing automated tests is a time-consuming and complex process.
2. Need for Continuous Integration:
A continuous informal action server must monitor the central repository and run the tests automatically for pushed new commits. Continuous integration simultaneously increases efficiency and costs.
3. Merge the Changes:
Software engineers must merge the changes as often as possible, at least once daily. There is a need to be more vigilant about these changes and to keep the central repository updated.
Benefits of Continuous Integration:
In this section, I have written the most essential benefits of Continuous Integration:
1. Makes the Production Smother and Error-Free:
Captured and staged bugs convey fewer bugs to production. It makes the production smoother and error-free. It increases the production rate.
2. Makes the Release Easy:
Continuous Integration speeds up releases by fixing errors early. Fixed bugs and tested early.
3. Less Context Switching:
It involves less context switching as software developers are vigilant and intimated about bugs and issues. Before starting another task, overcome these concerns. It avoids unusual switching and saves the time and cost of the development.
4. Minimal Testing Costs:
Continuous Integration server can perform hundreds of tests in seconds, reducing testing costs.
5. Betterment of Overall Quality Culture:
The quality assurance team spends less time on testing and can focus on the overall development of an organization’s quality culture.
Continuous Delivery (CD)
Continuous delivery is an approach in software engineering that allows the teams to develop the software in short cycles or parts.Automated deployment and production-like software production ensure stringent software release control. Key features are stated below:
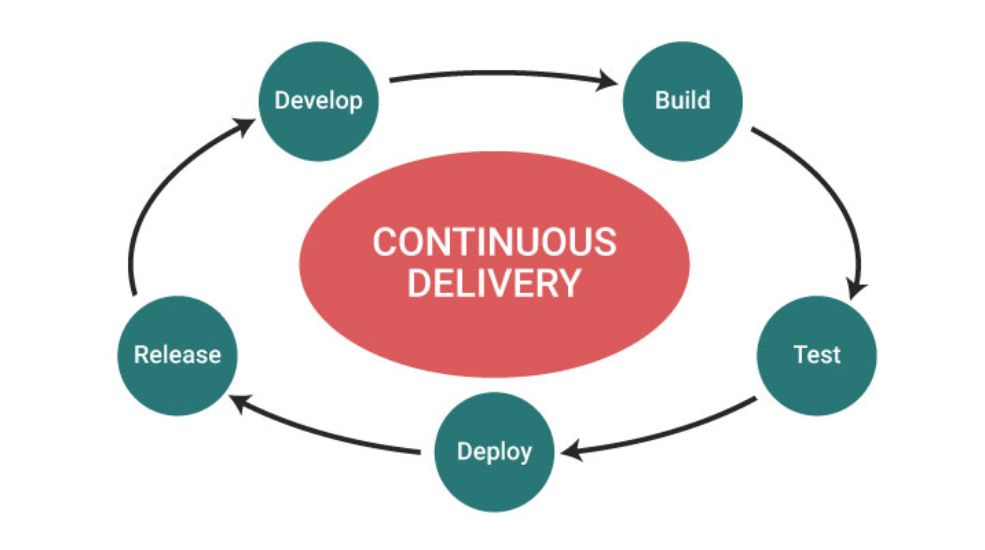
Key Features of Continuous Delivery:
Continuous Delivery (CD) key features are given below in detail.
1. A Strong Base of Continuous Integration:
Developers need a strong base of Continuous Integration. The test suite must be able to cover the codebase. Developers need to develop robust testing procedures under Continuous Integration.
2. Automated Deployments:
Continuous Integration requires automated deployment. Activation is manual, but after the initiation of deployment, there is no need for human intervention. Continuous integration comes at a higher speed as it avoids human intervention.
5. Feature Flags:
Developers need to embrace Feature flags. It enables the system to ensure that incomplete features do not affect production. It helps in building an efficient production system. Further, developers may quickly identify preliminary or underprocess features.
Benefits of Continuous Delivery:
You can read the benefits in the below section.
1. Erasing Complexity:
Continuous delivery removes the hurdles and complexity of deploying software. Developers don’t need to spend days preparing for release. It makes the delivery and deployment of software easy and quick.
2. Feedback and Upgradation:
Continuous delivery involves continuous upgradation or continuous release. It enables the developers to get customer feedback and accelerate feedback-driven software improvements. It increases efficiency and makes customers happy.
3. Small Changes with Significant Outcomes:
Developers need to keep upgrading the small changes in the software to improve the overall performance. There is less pressure for small changes; it encourages easy and quick upgradation. Collectively, these tiny changes result in significant outcomes in the form of improvements.
The Final Verdicts:
Despite this distinction between CI and CD, DevOps aims to generate high-quality consumer software and apps. Developers benefit from continuous integration in the first stage of code delivery and continuous deployment or delivery in the second. CI develops code for release, while CD releases it.
Deploying changes to production is easy for a new project without users. Launch the alpha version without clients using automated deployments. Customer-facing apps need continuous integration and delivery. Instead of end-to-end testing, write simple automated tests. Prioritize automatic deployments.